Homocysteine: Structure, Function, and Importance
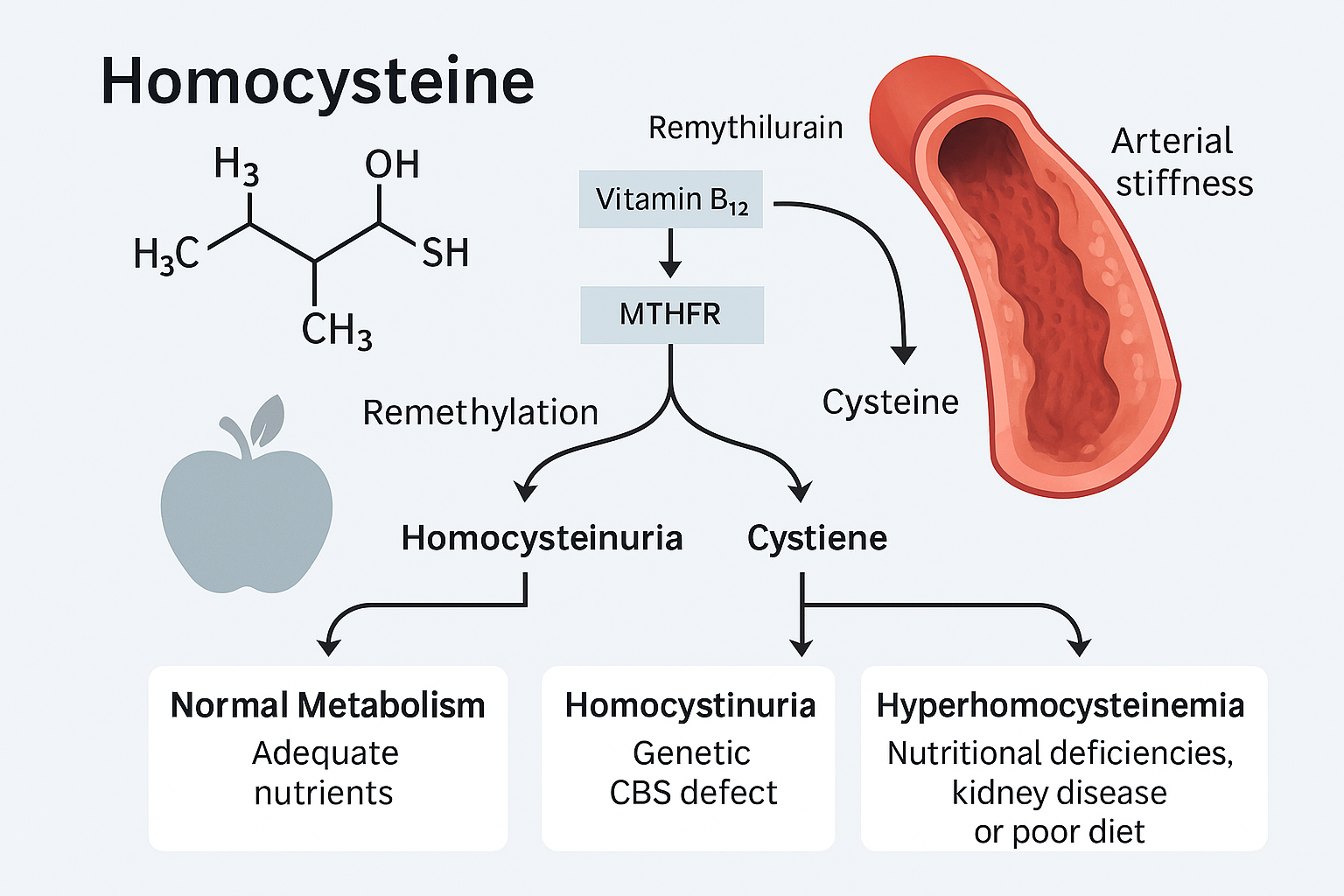
Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid that is produced in the body during the metabolism of methionine, an essential amino acid obtained from dietary protein. It is not found in the diet and does not have a specific function in protein synthesis. Instead, homocysteine serves as an intermediate in several critical biochemical pathways, particularly the…